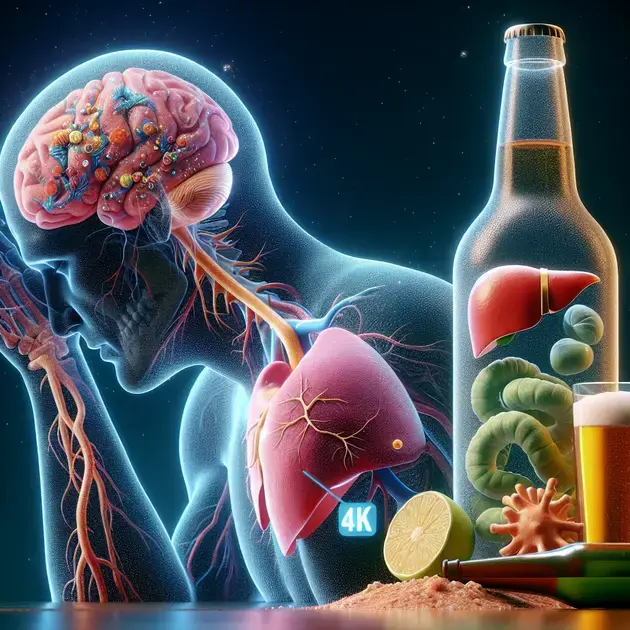
Understanding the Effects of Alcohol on Your Body is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. With alcohol consumption being a common part of social gatherings and celebrations, knowing how it impacts your body can help you maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Recent studies have shown that alcohol can have both short-term and long-term effects on various organs in your body, including the brain, liver, and heart. By understanding these effects, you can better protect your health and well-being in the long run.
Alcohol’s Impact on the Brain and Body
Alcohol exerts various effects on the brain and body, affecting both physical and cognitive functions. The short-term impact of alcohol consumption can be particularly notable, leading to changes in behavior, coordination, and overall well-being. Understanding these effects is crucial for making informed decisions regarding alcohol consumption.
Short-Term Effects of Alcohol on Organ Function
When alcohol is consumed, it rapidly enters the bloodstream and is distributed throughout the body, affecting various organs. One of the primary organs impacted by alcohol in the short term is the liver. The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing alcohol, and excessive drinking can lead to liver inflammation and damage.
Additionally, alcohol can affect the gastrointestinal tract, leading to issues such as acid reflux and irritation of the stomach lining. This can result in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and indigestion shortly after alcohol consumption.
Another organ affected by alcohol in the short term is the brain. Alcohol acts as a depressant on the central nervous system, causing impairments in cognitive function, coordination, and decision-making. This can manifest as slurred speech, impaired judgment, and decreased inhibitions.
To mitigate the short-term effects of alcohol on organ function, it is essential to drink in moderation and stay hydrated. Using apps like DrinkControl or AlcoDroid can help track alcohol consumption and set limits to avoid overindulgence.
Long-Term Health Risks of Alcohol Consumption
While the short-term effects of alcohol on organ function are concerning, the long-term health risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption are even more alarming. Chronic alcohol abuse can have detrimental effects on various organs, including the liver, brain, heart, and pancreas.
Prolonged alcohol use can lead to liver cirrhosis, a serious condition characterized by scarring of the liver tissue. This can ultimately result in liver failure, impacting the body’s ability to function properly and leading to severe health complications.
Furthermore, alcohol consumption over an extended period can cause cognitive impairments, memory loss, and an increased risk of developing neurological disorders such as dementia. The brain’s structure and function can be significantly altered by alcohol abuse, affecting mental clarity and overall cognitive abilities.
To address the long-term health risks of alcohol consumption, seeking support from healthcare professionals or support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous can be beneficial. Utilizing resources like the Ria Health app for telemedicine services can also aid in managing alcohol use and promoting healthier habits.
**The Link Between Alcohol and Mental Health**
Alcohol consumption has long been associated with mental health issues, and research continues to highlight the link between the two. Studies have shown that excessive drinking can contribute to the development or exacerbation of various mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. The effects of alcohol on the brain can lead to changes in mood, behavior, and cognitive function, making individuals more vulnerable to mental health disorders.
Furthermore, the use of alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress or emotional pain can create a cycle of dependence that further impacts mental well-being. This reliance on alcohol to manage emotions can contribute to the development of substance use disorders and complicate the treatment of underlying mental health issues.
It is important for individuals struggling with their mental health to be mindful of their alcohol consumption and seek support when needed. By addressing both the mental health concerns and the drinking habits, individuals can work towards holistic recovery and improve their overall well-being.
Overall, understanding the link between alcohol and mental health is crucial for promoting mental wellness and providing effective support to those in need. By raising awareness of this connection, we can encourage healthier habits and reduce the stigma surrounding mental health and substance use.
Exploring the Physical Effects of Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption not only affects mental health but also has significant physical repercussions on the body. From the moment alcohol is ingested, it begins to impact various organs and systems, leading to both short-term and long-term effects.
One of the most immediate effects of alcohol consumption is its impact on the liver. The liver works to metabolize alcohol, and excessive drinking can result in inflammation, fatty liver disease, and even cirrhosis over time. This can have serious implications for overall health and longevity.
Additionally, alcohol can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Chronic alcohol abuse can disrupt the balance of immune cells in the body, reducing the body’s ability to fight off pathogens effectively. This can result in frequent illnesses and slower recovery times.
Furthermore, alcohol can contribute to cardiovascular issues, such as high blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms. Prolonged alcohol abuse can damage the heart muscle and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. These physical effects highlight the importance of consuming alcohol in moderation and being mindful of its impact on overall health.
Raising Awareness: Alcohol’s Impact on the Immune System
The immune system plays a crucial role in defending the body against infections and diseases, but alcohol consumption can compromise its functions. Excessive drinking can impair the immune response, making individuals more vulnerable to illnesses and reducing the body’s ability to recover effectively.
Alcohol affects the production and function of immune cells, such as white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off pathogens. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to a weakened immune system, increasing the risk of infections, including respiratory infections, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
Moreover, alcohol can disrupt the gut microbiome, which plays a key role in immune function. Imbalances in the gut flora due to alcohol consumption can lead to systemic inflammation and further weaken the immune response. This can have widespread implications for overall health and well-being.
By raising awareness of alcohol’s impact on the immune system, we can educate individuals on the importance of moderation and responsible drinking. Supporting a healthy immune system through lifestyle choices, such as limiting alcohol consumption, can help maintain overall health and reduce the risk of infections and diseases.
Conclusion
Alcohol consumption has a significant impact on mental health, with research consistently highlighting the connection between excessive drinking and conditions like depression and anxiety. The effects of alcohol on the brain can alter mood, behavior, and cognitive function, increasing vulnerability to mental disorders. Additionally, using alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress can lead to dependency, complicating the treatment of both substance use and mental health issues.
It is crucial for individuals facing mental health challenges to monitor their alcohol intake and seek appropriate support. Addressing both mental health concerns and drinking habits is essential for comprehensive recovery and enhancing overall well-being. By understanding the relationship between alcohol and mental health, we can promote mental wellness, encourage healthier habits, and reduce the stigma associated with substance use and mental disorders.
Furthermore, alcohol consumption not only affects mental well-being but also has profound physical consequences. From liver damage to immune system impairment and cardiovascular issues, excessive alcohol intake can have serious health implications. By being mindful of alcohol consumption and its impact on the body, individuals can take steps toward maintaining good health and reducing the risk of illnesses and diseases.