“`html
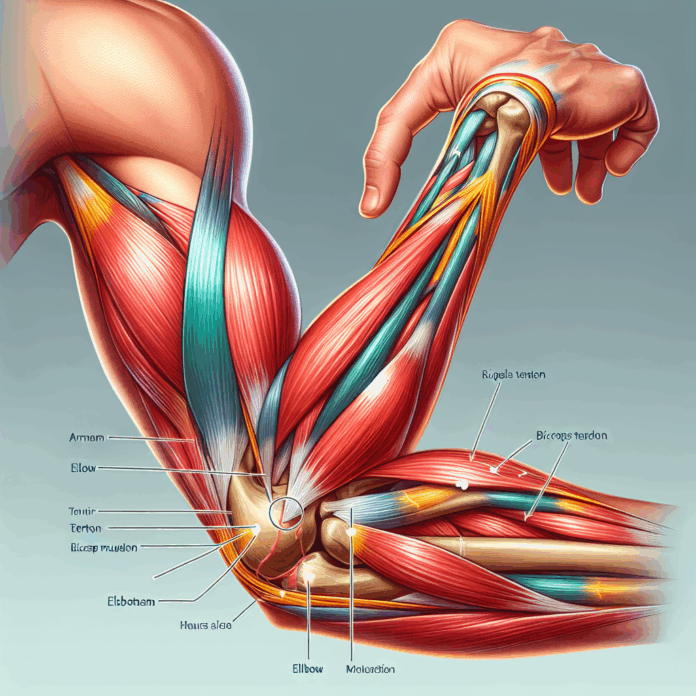
A distal biceps tendon rupture is an unfortunate and often painful injury, particularly prevalent among active adults, where the bicep muscle detaches from its lower connection at the elbow. In the latest video from Ask the Doctor series, Dr. David Guyer, a triple board-certified orthopedic surgeon and sports medicine specialist, delves into the mechanics of this injury, exploring how it occurs, the telltale signs, and why it often requires surgical intervention. From unexpected mishaps like lifting a heavy couch or a slip during a workout, eccentric loads imposed on the bicep can lead to this rupture, leaving distinct symptoms such as significant bruising and the infamous “Popeye deformity.” This blog aims to expand on Dr. Guyer’s insights, offering a detailed exploration of the causes behind this injury, the typical symptoms one might experience, and the crucial steps to take if you suspect you’ve suffered a distal biceps tendon rupture—knowledge that can guide many towards a timely medical evaluation and recovery path.
How Does a Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture Occur?
The distal biceps tendon rupture typically occurs when an eccentric load is applied to the biceps. This means that while the bicep is contracting during movement, a force in the opposite direction causes the tendon to tear from its attachment below the elbow. To break it down:
- Eccentric Load: The biceps are often engaged in a concentric motion, such as lifting a weight. However, if an external force extends the elbow rapidly, it can cause the tendon to tear.
- Common Scenarios:
- Lifting heavy objects: Imagine hoisting a heavy sofa. If it slips, one instinctively keeps holding on, but the sudden extension of the arm while contracting the bicep can lead to a rupture.
- Gym accidents: Preacher curls, where the arm is on a bench and curling weights, are notorious. If the weight slips unexpectedly, the sudden jerking motion can easily pull the tendon off the bone.
- Age Groups at Risk: The injury is mostly seen in those in their 30s who are very active, and in a broader age group from their 50s to 70s. While younger individuals may suffer due to intense physical activities, older adults are at risk due to age-related tendon weakening.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Once a distal biceps tendon rupture occurs, the symptoms are usually apparent. Knowing these signs can help in seeking timely medical intervention:
- Immediate “Pop” Sensation: Many who experience this injury report a distinct popping sensation in the elbow at the time of injury.
- Bruising and Swelling: Shortly after the injury, significant bruising appears in the lower arm and bicep region, accompanied by swelling as the area responds to the trauma.
- The “Popeye Deformity”:
- Named after the famous cartoon character, the “Popeye deformity” describes the abnormal bulging of the bicep after the tendon detaches. Despite Popeye’s famously large forearms, the term has stuck to describe how the muscle balls up when the tendon is retracted.
- Loss of Strength and Function: With the tendon rupture, individuals often find a noticeable decrease in arm strength, particularly when it comes to turning the arm or lifting heavy objects.
Seeking Treatment
When faced with a distal biceps tendon rupture, prompt medical evaluation is critical. Here’s what typically follows:
- Consulting an Orthopedic Surgeon: Suspected cases should be evaluated by an orthopedic specialist. In many instances, a physical examination is sufficient to diagnose the rupture without needing an MRI.
- Surgical Intervention: For active individuals, surgery is often recommended to reattach the tendon and restore full functionality. Ideally, this should be performed within the first few weeks post-injury to ensure the best outcomes and minimize complications.
- Non-surgical Options: While surgery is the preferred route for those seeking to maintain an active lifestyle, non-operative management may be considered for less active individuals. This could involve physical therapy and strengthening exercises, although it might not restore full strength or function.
Taking Precautions and Moving Forward
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some measures to minimize the risk of distal biceps tendon rupture:
- Proper Exercise Techniques: Practicing proper form and techniques in weightlifting and other physical activities can prevent undue stress on the tendons.
- Recognizing Risks in Daily Activities: Being mindful of body mechanics while lifting or pulling heavy objects can avert unexpected injuries.
- Strength and Flexibility Training: Incorporating exercises that strengthen the supporting muscles around the elbow and promote flexibility can offer better resilience to tendon injuries.
In sum, a distal biceps tendon rupture is a significant injury with a distinctive cause, noticeable symptoms, and a clear treatment pathway. Awareness and education are key. For those at risk, understanding the mechanics behind such injuries and being proactive in seeking medical advice can make a substantial difference in recovery and long-term functionality. Whether through surgical or non-surgical means, a carefully orchestrated treatment plan can help individuals return to their former form and strength, ensuring that they continue their pursuits with confidence and capability.
“`