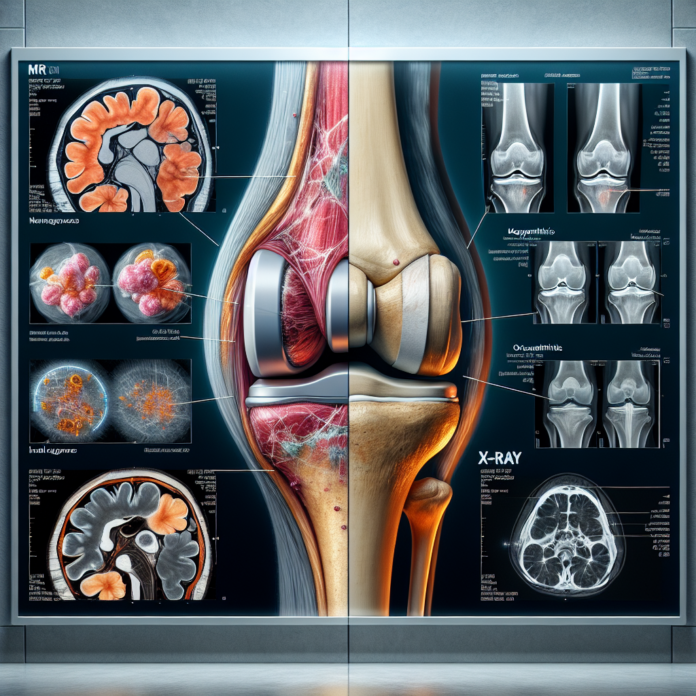
When it comes to diagnosing and evaluating the severity of osteoarthritis, the dilemma often lies in choosing the most effective imaging test. Should patients opt for a traditional set of X-rays or the more detailed MRI? This blog seeks to unravel the unique merits and limitations of each option, drawing from my insights as Dr. David Guyer, an experienced orthopedic surgeon. While X-rays provide a clear view of bone alignment and joint space, MRI scans offer a comprehensive look at soft tissues and cartilage condition. However, neither test alone should dictate treatment decisions, such as hip or knee replacements; clinical symptoms and patient experiences are equally pivotal. This discussion promises to guide you in making informed choices about your osteoarthritis management journey.
X-Rays: The Traditional Approach
X-rays have been the cornerstone of imaging for joint disorders, including osteoarthritis, for many years. They offer several advantages:
- Bone Visualization: X-rays excel at depicting the structure and alignment of bones. They show the density, contours, and any deformities in the bones, which are crucial for diagnosing joint degeneration.
- Joint Space Assessment: One of the key indicators of osteoarthritis is the narrowing of joint space due to cartilage loss. X-rays provide a clear view of this space, helping to assess the extent of cartilage wear indirectly.
- Detecting Bone Changes: They also reveal bone spurs (osteophytes) and sclerotic changes in the bone, both of which are common features of osteoarthritis.
However, there are some limitations to using X-rays:
- Soft Tissue Limitations: X-rays cannot show soft tissues like cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. Thus, they may not provide a full picture of the joint health.
- Two-Dimensional Images: X-rays are two-dimensional, which can sometimes limit the clinician’s ability to fully understand the complexities of the joint structure.
MRIs: A Comprehensive Perspective
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an advanced imaging technique that offers a more detailed view of both soft and hard tissues. Its benefits include:
- Detailed Soft Tissue Imaging: MRIs provide a detailed view of cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and the meniscus, which is beneficial in assessing the overall joint health and detecting specific issues like cartilage defects.
- Visualizing Cartilage: MRIs can show the thickness of cartilage and detect any tears, thinning, or damage, offering a direct assessment rather than inferring from joint space as with X-rays.
- Identifying Subtle Changes: They are sensitive to subtle changes in the bone marrow and can detect early signs of osteoarthritis that might not be visible on X-rays.
Despite these benefits, MRIs also have drawbacks:
- Cost and Accessibility: MRIs are more expensive than X-rays and may not be immediately accessible in all clinical settings.
- Static Nature: Since MRIs are conducted with the patient lying down, the absence of weight-bearing forces can sometimes make the degree of osteoarthritis appear less severe.
Choosing the Right Test
The decision between using an X-ray or an MRI should be guided by a variety of factors:
- Severity and Nature of Symptoms: For straightforward cases of osteoarthritis with classic symptoms, X-rays might suffice. However, for complex cases or when soft tissue involvement is suspected, an MRI can provide additional insights.
- Clinical Considerations: Treatment decisions, such as whether to proceed with joint replacement surgery, should not be based solely on imaging. They should also consider the patient’s symptoms, physical findings, and how the condition impacts daily activities.
- Cost and Time Constraints: In some cases, an X-ray may be used as a preliminary assessment due to its lower cost and quicker availability, with an MRI reserved for more detailed evaluations if needed.
Integrating Imaging with Clinical Evaluation
While imaging provides invaluable insights, it is just one piece of the puzzle. A comprehensive assessment of osteoarthritis involves:
- Thorough Clinical Evaluation: A detailed history and physical examination are fundamental to understanding the condition’s impact on the patient.
- Consideration of Patient History: Patient-reported outcomes, including pain levels, functional limitations, and prior treatments, play a critical role.
- Holistic Treatment Planning: The best treatment plans integrate imaging findings with patient preferences and clinical insights to offer personalized care.
In conclusion, both X-rays and MRIs have their place in diagnosing and assessing osteoarthritis. The choice between them depends on the specific clinical context and the detailed information required. With a balanced approach that considers both imaging results and clinical evaluation, healthcare providers can offer more targeted and effective treatment strategies for patients with osteoarthritis.