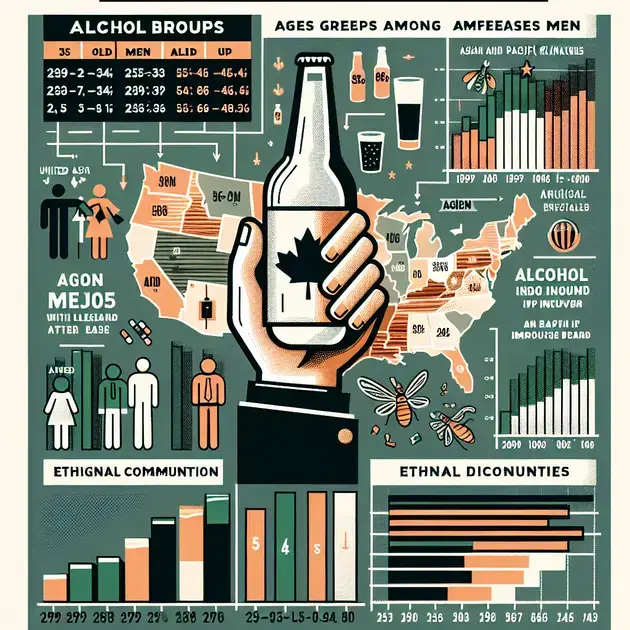
Alcohol-Related Deaths in the United States
Alcohol-related deaths in the United States have reached alarming levels and have nearly doubled from 1999 to 2020. This significant increase is particularly concerning for individuals aged 25 to 34, as their alcohol-related deaths have nearly quadrupled during this time period. Surprisingly, it is among those aged 55 to 64 that the highest rates of alcohol-related deaths are observed.
The statistics show that men consistently have higher rates of alcohol-related deaths compared to women. However, it is important to note that women have experienced the largest proportional rise in alcohol-related deaths, with a staggering increase of 2.5 times.
When examining the impact of alcohol-related deaths on different ethnic communities, Asian and Pacific Islander communities have faced the steepest increase. This finding underscores the need for targeted interventions and support for these communities.
Regionally, the Midwest has experienced the greatest rise in alcohol-related deaths, with rates increasing 2.5 times. Following closely behind are the Northeast, West, and South regions.
While the complete article may provide more in-depth analysis and evidence, these key findings highlight the urgent need for effective measures to address the escalating alcohol-related deaths in the United States. It is crucial to implement targeted interventions, educate communities about the risks associated with alcohol consumption, and provide accessible support and resources for those struggling with alcohol addiction.
As the impact of alcohol-related deaths continues to rise, it is imperative that policymakers, healthcare professionals, and communities work together to tackle this public health crisis. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to alcohol-related deaths and promoting healthier behaviors, we can strive towards reducing these alarming statistics and saving lives.