“`html
When it comes to maintaining an active, fulfilling lifestyle, injuries can be a major setback—especially those as intricate and painful as a distal biceps tendon rupture. This blog delves into the nuances of this specific elbow injury, which, despite its complexity, can often be traced back to common activities involving an eccentric load on the arm. Based on insights from Dr. David Guyer, a renowned orthopedic surgeon and sports medicine specialist, we explore how this injury occurs, the classic signs and symptoms to watch for, and why early medical intervention is crucial. Whether you’re in your 30s, continuously pushing your physical limits, or navigating the robust activities of your 50s and beyond, understanding this injury is vital. Dive in to learn more about the mechanisms behind distal biceps tendon ruptures and how you can better protect your elbows for continued strength and well-being.
How Does a Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture Occur?
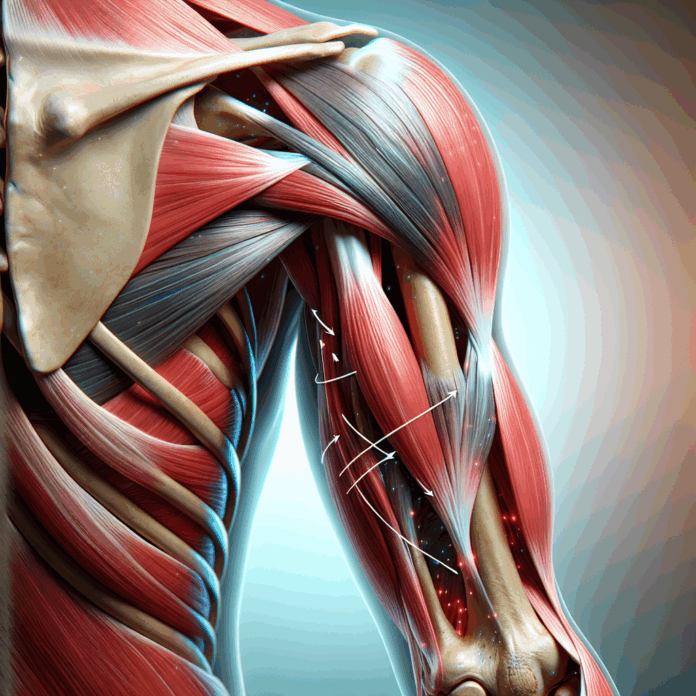
A distal biceps tendon rupture is a significant injury that can dramatically affect an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks, particularly for those who lead an active lifestyle. This condition occurs when the tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the elbow—specifically the lower part of the arm—tears away from the bone. Understanding the mechanisms behind this injury, recognizing its signs and symptoms, and knowing when to seek treatment are pivotal for a successful recovery.
The biceps muscle, which is located at the front of the upper arm, is critical for numerous activities that involve lifting or moving objects. Two tendons attach this muscle to the bones: the proximal tendon at the shoulder and the distal tendon at the elbow. A rupture often results from an “eccentric load,” where the muscle lengthens while contracting. This type of load is experienced during activities that force the arm’s movement in an unexpected or forceful manner.
For instance, you might be lifting a heavy object such as a couch, and it suddenly slips, pulling your arm straight while your bicep is still attempting to hold the weight. Similarly, engaging in weightlifting exercises where the arm may lose grip or control, such as a preacher curl, can result in the tendon being forcibly yanked from the bone. These scenarios highlight how unexpected force can overload the tendon leading to a rupture.
Who Is at Risk?
While a biceps tendon rupture can happen to anyone, it commonly occurs in two distinct age groups. Younger individuals in their 30s and those between 50 to 70 years old are more susceptible. Younger people may suffer from these injuries due to high-intensity physical activities, while older adults might experience them because of tendon degeneration over time.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Rupture
A key indicator of a distal biceps tendon rupture is a sudden “pop” felt or heard in the elbow, followed rapidly by several other symptoms:
- Bruising and Swelling: Noticeable bruising typically appears in the lower arm or near the elbow. This bruising is accompanied by swelling in the bicep region.
- Popeye Deformity: A well-known sign of this injury is a visible bulge in the bicep muscle, often referred to as the “Popeye deformity.” This occurs because the tendon retracts, causing the muscle to bunch up.
- Weakness in the Arm: A person may experience significant weakness, especially when trying to rotate the forearm or flex the elbow.
- Pain and Tenderness: The injured area will often be tender and painful to touch.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to restoring normal function and preventing long-term complications. Surgery is often recommended, especially for active individuals, to reattach the tendon to the bone. Ideally, this surgical intervention should occur within the first few weeks following the injury to ensure optimal recovery.
Visiting an orthopedic surgeon for an assessment as soon as possible increases the likelihood of a successful outcome. While imaging tests like MRI can confirm the diagnosis, many experienced surgeons can determine the presence of a rupture through a physical examination alone.
Avoiding Distal Biceps Tendon Ruptures
Preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of such injuries. These include:
- Maintaining Strong and Flexible Muscles: Regular exercise that includes strength training and stretching can help protect tendons from injury.
- Proper Technique: Whether lifting weights or moving heavy objects, using the correct form and technique can prevent undue stress on the tendons.
- Wearing Protective Gear: In sports or activities where the risk of falls or extreme force exists, wearing appropriate elbow supports can mitigate injury.
Understanding a distal biceps tendon rupture is necessary for those who wish to maintain an active lifestyle without interruption. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent further damage and enhance recovery. Armed with the right knowledge, prevention strategies, and a keen eye for symptoms, active adults can protect themselves from the setbacks of such an injury and continue to enjoy their daily activities with confidence and safety.
“`