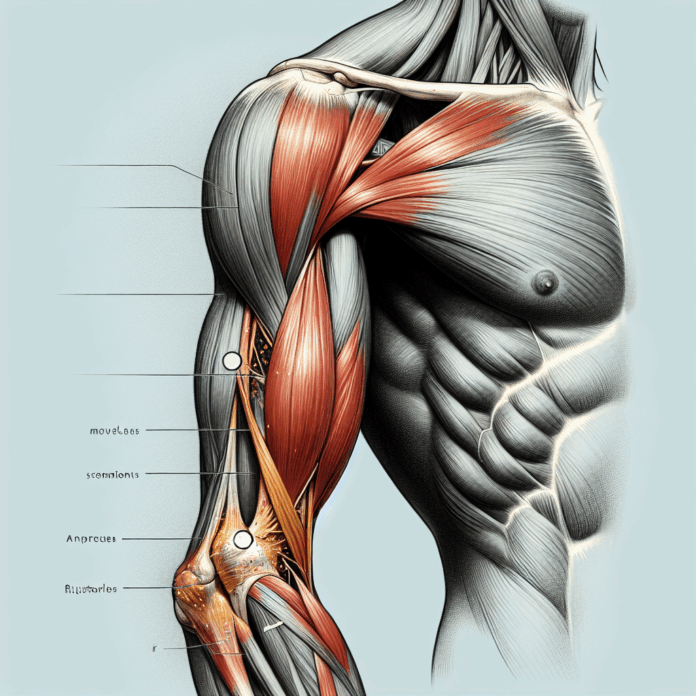
A distal biceps tendon rupture is an injury that can unexpectedly halt the active lifestyle of many adults, leaving them searching for answers and paths to recovery. In this blog, we delve into the mechanics of this injury, often characterized by a sharp ‘pop’ in the elbow and the subsequent appearance of the notorious “Popeye deformity.” With insights from Dr. David Guyer, a seasoned orthopedic surgeon, we explore the typical causes of this rupture, which frequently occur in active individuals aged between their 30s and 70s. Whether you’re an enthusiastic weightlifter or someone simply engaged in heavy lifting tasks, understanding the risks and signs associated with this injury is crucial. Join us as we unpack the dynamics of eccentric loads, the role they play in these painful and inconvenient ruptures, and why timely medical attention is vital for optimal recovery.
Causes and Mechanism
Distal biceps tendon ruptures can occur unexpectedly during everyday activities or while engaged in physical exercises. The distal biceps tendon connects the biceps muscle to the radius bone just below the elbow, facilitating the movement of the forearm. The injury is more common in two distinct age groups: the 30s, often involving physically active individuals, and the 50s to 70s, where it might relate more to degenerative changes in the tendons.
The main mechanism that leads to the rupture of the distal biceps tendon involves an eccentric load. During an eccentric contraction, the muscle lengthens as it contracts, often while lowering a weight or resisting a force that is extending the elbow. Imagine you’re lifting a heavy object when suddenly it slips, forcing your arm to straighten out abruptly. This unexpected force can cause the biceps tendon to tear away from its attachment on the radius.
Common Scenarios Leading to Rupture
- Heavy Lifting at Home or Gym: Imagine carrying a couch up a flight of stairs, and it slips from your grip. The biceps tendon, actively engaged in holding the weight, is suddenly jerked backward, potentially causing a rupture.
- Preacher Curls in the Gym: When the arm is securely resting on a bench while performing bicep curls, a sudden slip of the weight or miscalculation in form can lead to a similar eccentric contraction, pulling the tendon off the bone.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a distal biceps tendon rupture is crucial for seeking timely intervention. Typical signs include:
- A Sudden ‘Pop’: Many individuals report feeling or even hearing an audible pop when the tendon ruptures, followed by immediate pain in the elbow.
- Bruising and Swelling: Within a short period, significant bruising can develop in the lower part of the arm and the elbow region, signaling internal bleeding from the torn tendon.
- Popeye Deformity: A retracted biceps muscle causes the characteristic swelling akin to a bulging bicep, reminiscent of the cartoon character Popeye. This occurs because the torn tendon allows the muscle to bunch up.
- Weakness or Inability to Lift: Following a rupture, you might find it difficult to turn your forearm or lift objects as you usually would.
Why Surgery is Often Recommended
For active individuals, surgery is typically recommended to reattach the tendon to the radius. This reattachment is crucial not only for restoring the full function of the arm but also to prevent lasting deformity and weakness. It is advised that this surgical intervention occurs within the first few weeks following the injury to optimize outcomes and minimize complications associated with delayed treatment.
Diagnostic Approach
A seasoned orthopedic surgeon can often diagnose a distal biceps tendon rupture through a physical examination without necessarily requiring MRI imaging. The distinct symptoms and physical changes in the arm provide clear indicators of the injury. Nevertheless, imaging can still be utilized to confirm the diagnosis or assess the condition of surrounding tissues.
The Importance of Early Medical Evaluation
Seeking professional evaluation promptly is critical. Delayed treatment can complicate the surgical repair process and potentially affect the long-term strength and function of the arm. If you suspect a biceps tendon rupture, consult an orthopedic specialist to discuss the best course of action. Early intervention will not only hasten recovery but also help mitigate the risks of chronic weakness and mobility limitations.
Additional Considerations and Prevention
While not all tendon ruptures can be prevented, understanding safe lifting techniques and maintaining general tendon health can reduce risk:
- Regular Conditioning: Strengthening the surrounding arm muscles and maintaining flexibility through regular exercise can provide better support to tendons during exertion.
- Proper Technique: Whether lifting weights or moving heavy objects, ensuring proper form can prevent unnecessary strain on tendons.
- Balanced Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a diet rich in nutrients essential for tendon health, can also contribute to minimizing risk factors associated with degenerative changes.
In conclusion, a distal biceps tendon rupture is a significant injury that requires prompt attention, particularly for those who lead active lives. The combination of eccentric load during physical activities, age-related tendon changes, and sudden unexpected movements all contribute to the risk of this debilitating injury. By recognizing the signs, seeking immediate medical evaluation, and understanding the importance of surgical repair, individuals can ensure a smoother path to recovery and return to their regular activities.