“`html
Plica syndrome is a condition that puzzles many, often leading to questions about its symptoms, treatment, and particularly why surgery isn’t readily embraced as a solution. Although it affects a noteworthy portion of the population, ranging from 5% to 25%, the discomfort it causes can vary significantly. This blog delves into the intricacies of plica syndrome, a condition marked by a snapping sensation and pain due to a band of tissue inside the knee. We’ll explore why orthopedic surgeons are cautious about rushing into surgical interventions, often opting for conservative treatments like anti-inflammatory therapies and physical therapy as initial approaches. Understanding these nuances can help individuals navigate their treatment options and make informed decisions on managing this often elusive source of knee pain.
Understanding Plica Syndrome
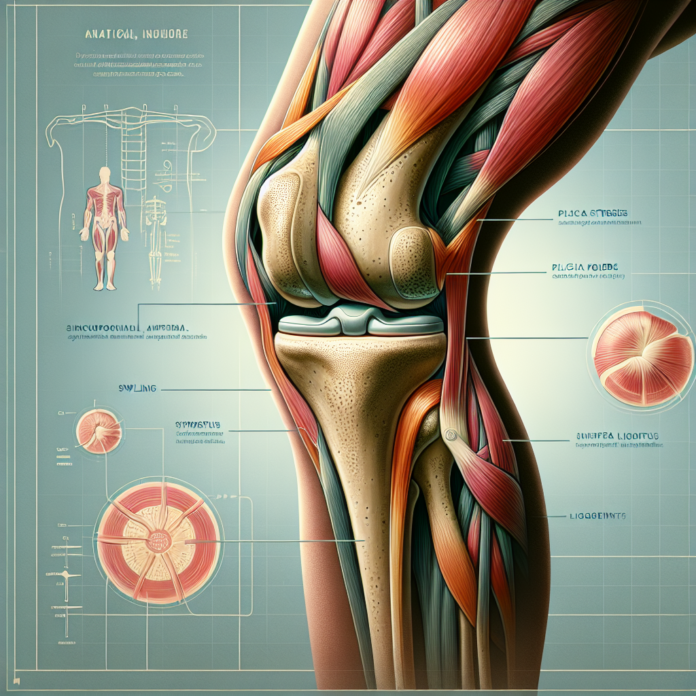
Plica syndrome is a fascinating yet often overlooked condition affecting the knee. It involves a band of synovial tissue inside the knee joint that becomes irritated and inflamed, causing discomfort and pain. Understanding this condition involves recognizing its prevalence and the nuanced approach required for diagnosis and treatment.
To delve deeper, it’s important to grasp that while a plica is a normal structure found in many knees, problems arise when it becomes inflamed. This inflammation can lead to the snapping sensation and pain during movement. The condition does not always present symptoms, which is why many individuals with a plica are asymptomatic and unaware of its presence.
Signs and Symptoms
- Snapping Sensation: One of the hallmark indicators of plica syndrome is a noticeable snapping or popping sensation inside the knee. This typically occurs during movement, such as bending or straightening the knee.
- Pain and Discomfort: The usual pain is localized, often felt on the inside of the knee. It can range from a mild discomfort to severe pain that affects daily activities.
- Swelling: In some cases, the inflammation can cause visible swelling around the knee joint.
Diagnosis
Orthopedic surgeons may suspect plica syndrome if these symptoms align with the patient’s clinical presentation. However, it’s crucial to rule out other potential causes of knee pain, such as meniscus tears or ligament injuries. Diagnostic imaging, like an MRI, can help identify a plica but might not necessarily show inflammation. Thus, a comprehensive physical exam and a thorough medical history are critical for diagnosis.
Why Do Surgeons Prefer Conservative Treatments?
The preference for non-surgical treatments stems from several reasons:
- High Prevalence of Asymptomatic Plicas: Many people live with a plica without experiencing any symptoms. The mere presence of a plica on an MRI doesn’t confirm it as the pain source.
- Variable Symptomology: Not every plica is symptomatic. Symptoms like snapping or pain can often be attributed to other knee pathologies, making it vital to ensure the plica is indeed the cause before considering surgery.
- Effectiveness of Non-Surgical Interventions: Treatments like anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy often prove effective. These options aim to reduce inflammation and improve knee function without the risks associated with surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Rest and Activity Modification: Sometimes, simply allowing the knee to rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate the symptoms can be beneficial.
- Physical Therapy: A tailored physical therapy program can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and reduce the mechanical strain on the plica.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, a localized steroid injection may be administered to directly reduce inflammation.
When Is Surgery Considered?
Surgery becomes an option predominantly when all other treatments fail to provide relief, and there’s a high degree of certainty that the plica is the pain source. Surgeons may opt for an arthroscopic procedure to remove the inflamed tissue in these cases. However, surgery is rare and generally reserved for cases with significant and persistent symptoms.
- Surgical Procedure: Plica resection is done arthroscopically. This minimally invasive technique allows for a quicker recovery and less postoperative pain. The goal is to remove the inflamed plica tissue and address any other issues identified during the procedure.
- Post-Surgical Considerations: Patients should be aware of potential postoperative swelling and the need for a comprehensive rehabilitation program to restore full knee function following surgery.
Conclusion
Plica syndrome requires a nuanced understanding, with diagnosis and treatment tailored to each patient. The general hesitation toward surgery stems from the desire to avoid unnecessary procedures, especially when non-surgical treatments offer relief and are successful for many individuals. By focusing on conservative measures first, orthopedic specialists aim to manage symptoms effectively while keeping surgical interventions as a last resort.
For those dealing with persistent knee pain, consulting a knowledgeable orthopedic surgeon who can navigate these complexities is crucial. By working closely with medical professionals, patients can better understand their condition and explore all potential treatment avenues to achieve the best possible outcomes.
“`